In this article, we are going to discuss concrete blocks and its advantage and disadvantages, and many more.
Many centuries ago people have changed and adjusted to many structures, like caves, etc.
They begin a journey to create accommodation for themselves.

Along with the emergence of culture and civilization, people go about to settle & build their own accommodation.
There are different types of residence according to their culture, taste, environments, and available materials.
Likewise, the structure of a building is just not a house for living.
It has many parts which give the building its safety & identity, character, strength, like its foundation, stair, wall, floor, roof, etc.
The building or home has various sections like bedroom, living room, kitchen, bathroom, washroom, storeroom, etc.
Before the beginning of advanced technology, most construction is built with red bricks, stones, mortar, & wood.
Not that the only materials that contribute to creating a structure but Concrete is also used extensively for build a long-lasting building.
A few main masonry unit types are:
Nowadays Concrete blocks are used widely as normal, red bricks are harmful to the environment.
Definition of Concrete Block
According to ‘David Blockley’, a Concrete Block is a ‘Building Block made totally of concrete.
which is then bonded together with Mortar to form an imposing long-lasting structure.
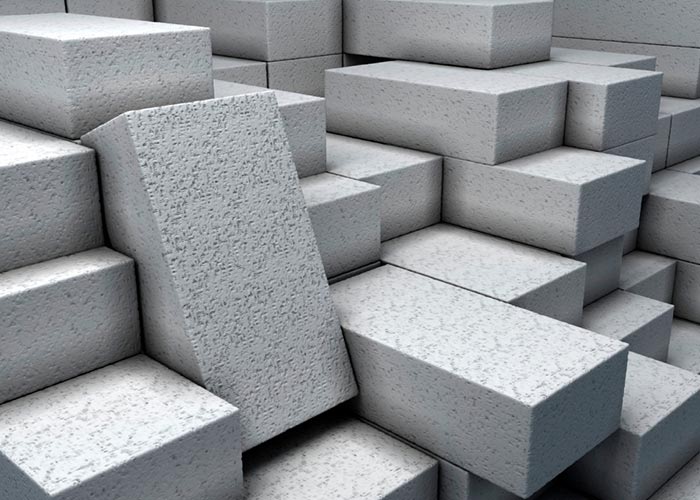
These types of buildings are made from ‘Hollow’ or ‘Solid’ blocks.
It can be ordinary and lightweight concrete in different standards sizes depends on requirements.
-
Hollow Concrete Blocks
-
Solid Concrete Blocks
Hollow Concrete Blocks are very often used than solid blocks because:
Hollow Blocks are not heavy and easy to handle.
They can be grout and reinforced, yet meets difficult structural needs easily.
Solid Concrete Blocks are disappearing nowadays, because of their added mass.
It only calls for special requirements or need, such as Higher Fire Resistance, where being impassable is of paramount signification.
Let us know more.
Solid Concrete Blocks
The overall dimensions of the Solid Concrete Blocks are more than 75% of the total mass fill up with concrete that is known as Concrete Brick.
Hollow Concrete Blocks
It having solid material of around 50-70% of the total volume, calculated from the overall dimensions is designate as a Hollow Concrete Block.
Hollow Concrete Blocks have single or more large holes.
which either passes through the open cavity or just might produce to reduce the mass but the cost of its strength.

Hollow Concrete Blocks are further sorted into two divisions, viz Grade A & Grade B.
This Grade B category has been occasionally referring to as Cinder Block, as the Cinder is the composite more often use in its material base.
The Hollow Concrete Blocks are nowadays are available in the market in different shapes & sizes.
As stated by its location or position in the wall.
These are Corner Concrete Blocks, Jamb Concrete blocks, Bullnose Concrete Blocks, Concrete Stretcher Blocks, Partition Concrete Blocks, Frogged Brick Blocks, Lintel Blocks, etc.
Pros of Concrete Blocks
Concrete blocks make a room bigger by expanding the carpet area on account of the decrease wall thickness owing to narrower Concrete Blocks than the standard brick masonry wall.
Concrete Blocks defend the interiors against noise pollution, as it soaks up the sound and it also protects against fire.
It provides superior thermal insulation.
Manufacture along with Concrete Block is faster, stronger, & structural as differentiate to the brick masonry due to the big size of blocks.
Concrete Blocks defend farmers’ land, which otherwise would have been burrow abundantly for manufacturing clay bricks.
As differentiate to conventional masonry building, Individual units can be produced to bigger custom size & shape, ensuring quick turnaround in construction cycle with fewer joints mortar consumption rate decrease, yet increase the gross robustness of the establishment.
Unlike standards bricks, Concrete Blocks’ costume size cuts down on plaster usage.
So it becomes an inexpensive viable choice.
There are a few more advantages & disadvantages of various Blocks, which are as given below.
The benefit of Solid Concrete Blocks
Relatively easier to design Solid Concrete Blocks.
These Blocks are highly resistant to utmost weather conditions, like storms, high winds, and floods, etc.
The benefit of Hollow Concrete Blocks
For reinforcement, Hollow Concrete Blocks does not need extra formwork or any special building machinery.
Fresher or semi-skilled labor can also easily do it finely.
Cons of Concrete Blocks
If the essential raw materials are not willingly convenient then this becomes a costly proposition product.
Labour should be experienced & skilled for the fast & stable production of Concrete Blocks.
Cons of Solid Concrete Blocks
It is difficult to make concealed wiring, plumbing in any structure.
Cons of Hollow Concrete Blocks
Hollow Concrete Blocks are risky during earthquakes if Without an internal reinforcement structure built.
Concrete Blocks Uses
These are perfect for extensive housing and different civil engineering projects.
Concrete Blocks applications:
Concrete Blocks for Building Walls
For fast and easy installation, partition walls advantage extremely by adopting utilization of Concrete Blocks.
Steel reinforcement gives extra strength to the construction.
Solid Concrete Blocks are right for Fireplaces & built of Chimney, yet they equally shine at Non-load Bearing & Garden Walls.
Hollow Concrete Blocks are extensively used for outdoor & indoor Load-bearing Walls, Boundary Walls, Panel Walls, Partition Walls, etc.
Used for the Formation of Material Bin
From different climatic conditions, Concrete Blocks can defend the stored materials.
No wonder, it remains engineers’ decision for the formation of Material Bins.
It helps in keeping the materials away from one another, that is why manufacturing companies choose to employ this.
They utilize these Concrete Blocks to reserve material for the long-term – like rock, aggregate, etc.
Concrete Blocks Utilized in Landscape Projects
Concrete Blocks also use in various applications.
For example, in Flower Bed, Outdoor Bar, Outdoor Seating, Decorative Screen, Patio designs & many Outdoor Furniture.
Concrete Blocks Properties
The different properties of Concrete Blocks are:
-
Dimensions
Dimension is the size of Blocks in the matter of Length, Width & Height.
Concrete Blocks are mention by their nominal dimensions.
‘nominal’ is dimensions that consist of the thickness of mortar joints.
Actual dimensions (Length and Height only) have to be 10 mm short of the formal dimensions.
For example, a 400 mm X 200 mm X 200 mm Block has actual Length, Width, and Height measures of 390 mm, 200 mm, and 190mm respectively.
As per the Indian Standard Code 2185, The formal dimensions of Concrete Block are:
Length: 400, 500 or 600 mm
Width: 50, 75, 100, 150, 200, 250 or 300 mm
Height: 100 or 200 mm
Other than the above referred Concrete Block sizes, they tend to differ extensively based on the mutual contract between the purchaser and the supplier.
-
Density
Density is the mass per unit volume of a solidity.
There is a parameter for describing the material and form of a mass in the existence of gravity.
The density of Concrete Blocks is:
Solid Concrete Blocks -1,800 kg/m3 (Minimum)
Hollow Concrete Blocks
Grade A – 1,500 kg/m3 (Minimum)
Grade B – 1,100 kg/m3 & 1,500 kg/m3
-
Compressive Strength
Compressive strength is the capability of a material to withstand compression.
The minimum average compressive strength of Concrete Blocks is:
Solid Concrete Blocks– 4.0 and 5.0 N/mm2
sequentially at 28 days
Hollow Concrete Blocks
Grade A – 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 7.0, 8.5, 10.0, 12.5 and 15.0 N/mm2 sequentially at 28 days
Grade B – 3.5 and 5.0 N/mm2 sequentially at 28 days
-
Water Absorption
Water Absorption is the capability of the material to absorb and retain water and the water absorption should be less than 10% by mass.
-
Drying Shrinkage
The drying depreciation of Concrete Blocks should be less than 0.06%.
-
Moisture Movement
The moisture movement arises because material repeatedly inflates due to the outcome of swelling and shrinkage.
Concrete Blocks’ moisture movement around less than 0.09%.
Raw Materials
The basic materials needed for the manufacture of Concrete Blocks are:
Cement
The types of cement used for the construction of Concrete Blocks are Portland Slag Cement, Portland Cement, Portland Pozzolana Cement, etc. It should observe its respective standard codes.
Aggregate
The aggregate of the distinct genres utilize varying degrees of success, and they include cinder, clinker, gravel, crushed stones, etc.
The aggregates are sort lists on the virtue of their weight, texture, or composition of a unit design.
The strength, texture, and price of Concrete Block rely on the attentive grading of the aggregate.
The stratification of the combined aggregate shall conform to the needs of Indian Standard Code 383.
Water
Potable water is the basic necessity in the production process of Concrete Blocks.
Additives or Admixtures
Additives or admixtures may add either as admixtures to the concrete mix or as additives to the cement during its construction process.
Admixtures or additives used in the manufacture of Concrete Masonry Units are:
Water decrease, accelerating, air-entraining, and superplasticizers conforming to Indian Standard Code 9103.
Waterproofing representatives follow Indian Standard Code 2645.
Where no appropriate Indian Standards are available, the additives or admixtures shall be utilize based on ASTM or British Standard.
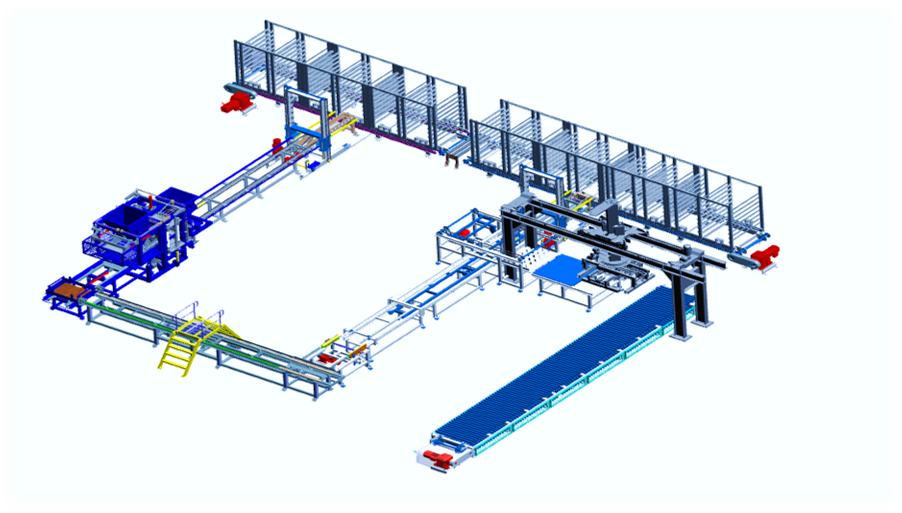
Making Process of Concrete Blocks
The manufacturing of Concrete Blocks consists of the following basic stages,

(I) Proportioning
The quantity of the material has been taking likewise the Indian Standard Code 2185 – or as per the robustness need.
(ii) Mixing
Batching of the ingredients should be done exactly and mixing shall be done in a mixture to gain a homogeneous mix.
It shall go on until there is a uniform circulation of the materials.
(iii) Compacting
The Block should be compact by Vibro compaction and accomplish to the proper size without any broken edges.
(iv) Curing
The Blocks shall cure in a curing water tank or curing yard and should keep repeatedly moist for at least 14 days.
When the Blocks are cure in an immersion tank, the water of the tank should change at least every 4 days.
(v) Drying:
After curing, the Blocks are dried for 2/3 weeks, and then only, they become fit to use for various intent.
If you do not follow it, diminution cracks are likely to show in walls.
Production of Concrete Blocks
The fully automatic plants are convenient for the manufacturing of high-strength Concrete Blocks.
These automatic machines produce superior quality Concrete Blocks, but they involve significant capital investment.
The manually operating machines are also obtainable and can even be installe in the project area.
This will dilute the transportation cost of the Concrete Blocks from the place of manufacturing to the place of actual use.
Conclusion
As specified previously, there is a large variation of masonry units from which an architect, owner, or engineer can choose the most suited for a particular circumstance.
As reported by Handbook on Masonry Design and Construction – SP 20 the primary discussion in choosing a particular unit are:
Dimensional Stability, Thermal Properties, Resistance to Rain Penetration, Fire Rating, Availability, Strength Requirement, Durability, Style of Architecture, and of course – Economy in Cost.
Concrete Blocks have been broadly using in buildings throughout the country.
Its properties such as Fire Resistance, Insulation, Durability, Strength & Structural Stability, and Sound Absorption make it acceptable for various types of applications.
Concrete Blocks are suitable in areas where brick or stone of sufficient quality for masonry are not available at a decent cost.
If proper variation of aggregates is available for manufacturing, they utilize masonry units for Blocks.
Which can utilize for load-bearing or even non-load-bearing walls, partitions, and panel walls.