How Concrete Blocks are Made?
The concrete blocks or cement bricks are building material used to build walls in the building. It is also known as a concrete masonry unit (CMU). The concrete blocks are one of the precast concrete products used for construction. Precast is the blocks are formed and hardened before they reach the job site. There are various concrete blocks and have one or more hollow cavities and the side may cast smooth or with design. These blocks are stacked with concrete mortar to make a wall.
The concrete mortar was first used by Romans in 200 B.C. for binding shaped stone in the building. In the Roman emperor, Caligula in 37-41 A.D. the small blocks of concrete as construction material in modern-day Naples, Italy. The concrete technology develops by Romans is lost with the fall of the Roman empire in the fifth century. An English stonemason Joseph Aspdin develop Portland cement in 1824.
The first hollow concrete block is designed by Harmon S. Palmer in 1890 in the United States and after 10 years of research and experiment, he patented the design in 1900. The block developed by Palmer was 8 x 10 x 30 inches and heavy that the crane is used to move.
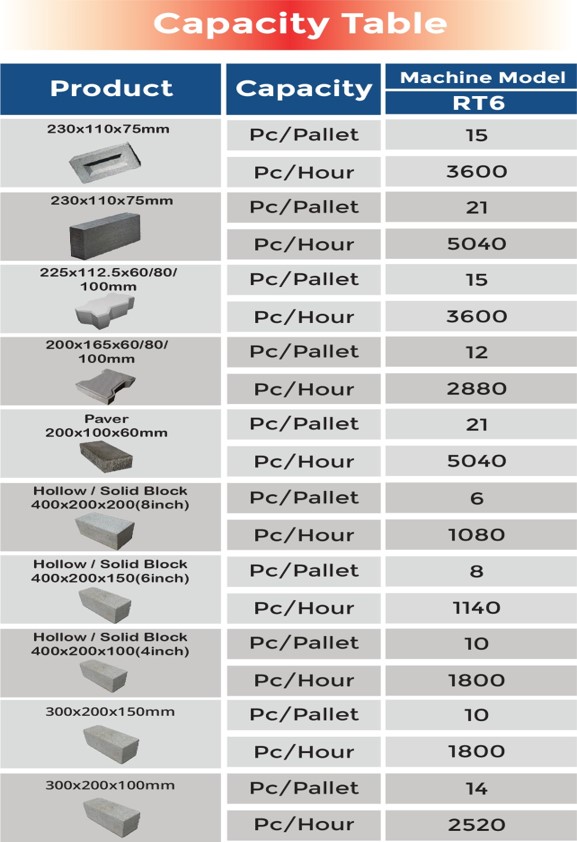
In this time there was an average 10 blocks made by one person and it was cast by hand. With modern-day machines and advanced technology, it is 2,000 blocks per hour.

Which Raw Materials are used?
For making the concrete bricks or blocks the raw material like a mixture of powdered Portland cement, water, sand, and gravel is used. These raw materials together make a light gray block having a fine surface texture and have high compressive strength. The weight of a typical concrete block is 38-43 lb (17.2 to 19.5 kg). There is a higher percentage of sand and a lower percentage of gravel and water for the blocks. This made very dry, stiff mixture and hold shape when removing from the block mold.
Different types of Raw Material
The cinder block is made with granulated coal or volcanic cinders. This is a dark gray block with a medium to coarse surface texture, having good strength and good sound-deadening property with high thermal insulating than the concrete block. The typical cinder block weighs around 26-33 lb (11.8-15.0 kg).
If there is granulated coal or volcanic cinders are used instead of sand and gravel with expanded clay, shale or slate the lightweight concrete block is made. The expanded clay, shale, and slate are made with crushing the raw materials and heating up to 2000o (1093o). The material is bloat or puffs up as there is rapid a generation of gases caused by the combustion of small particles f organic material inside. The light-weight concrete block weighs around 22-28 lb (10.0 to 12.7 kg) use to build a non-loading bearing wall and other partitions. Also, the blast furnace slag and natural volcanic materials like pumice and scoria are used for lightweight blocks.
Along with basic components, there is concrete mixture is used to make blocks contains a chemical called admixture for altering curing time and it increases the compressive strength or to improve workability. There are pigments added into blocks for uniform color or make the surface of the block uniform. This also protects the surface of a block from chemicals. The glaze on the block surface is made with a thermosetting resinous binder, silica sand, and color pigments.
Design of the Concrete Blocks
There are standardized shapes and sizes for common concrete blocks for building construction. The common block size is 8 x 8 x 16, as 8 inch high, 8 inches deep, and 16 inches wide. This measurement is including the bead of mortar and block measure is 7.63 in (19.4 cm) high, 7.63 in (19.4 cm) deep, and 15.63 in (38.8 cm) wide.
Many block manufacturers offer variation in block to look it aesthetically look better for particular applications. Like there is one concrete bricks or blocks manufacturer who designs blocks especially for water resistance through exterior walls. There is a split-faced block with rough, stone-like texture on one face of the block then the smooth face. These concrete bricks give a nice look aesthetically.
Manufacturing Process of Concrete Bricks or Blocks

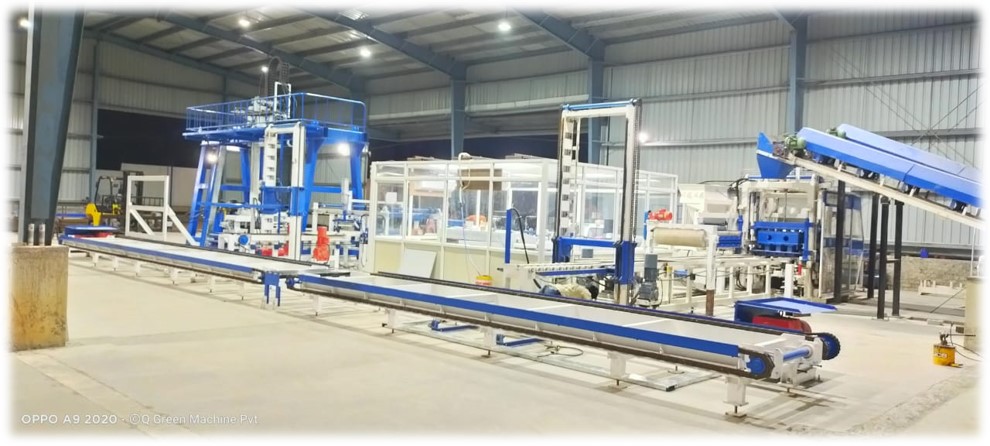
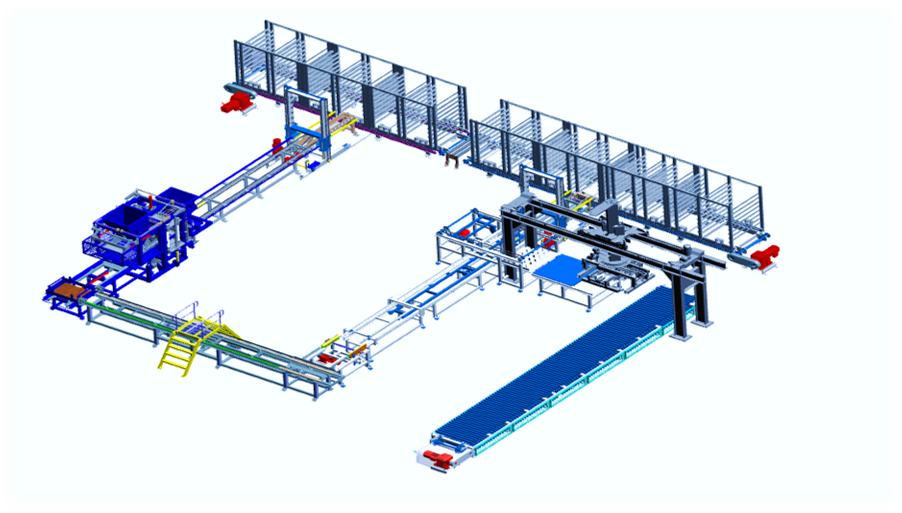
The concrete bricks manufacturing process consists of four steps: mixing, molding, curing, and cubing. There are concrete plants which only make concrete blocks while others produce a variety of precast products like blocks, flat paver, decorative pieces like lawn edging, concrete bricks, etc. With the advancement in technology some concrete brick making plants capable of making 2000 blocks per hour.
1.Mixing
Sand and gravel are stored in silos outside and then transfer through conveyor belt when needed and the cement is stored in silos to make it safe from moisture. When the mixing has started the sand, gravel and cement are coming out from silos via weighing batcher which weighs every material. The dry materials enter into a mixer where they are blended for a few minutes. There are mainly two types of mixers that use one is planetary or pan mixer also known as a shallow pan with a lid. The mixing blades are attached to a vertical rotating shaft with a mixer. Another type is a horizontal drum mixer. This is a coffee turned on the side and has mixing blades attach to the horizontal rotating shaft inside the mixer.
After the blending of dry materials, the small amount of water is added to the mixer. Now if the plant is located in warm places, the water is the first pass through heater or chiller to maintain the temperature. The mixing chemicals and color pigments added at this time and the concrete is mixed for six to eight minutes.
2. Molding
After the mixing, the concrete is dump into bucket conveyor and transported to an elevated hopper and the mixing cycle begins after the next load. After that, it is conveyed to other hoppers on the block machine at a controllable speed. Then concrete is downward to flow rate and it pours into molds. In the molds, there is an outer mold box that contains other mold liners. Liners have an outer shape of the block and inner shape of block cavities. There are 5 to 15 blocks are molded at one time depend on machine capacity.
After the mold filled with concrete, the hydraulic press compresses the concrete into the mold. The compression is complete by air or hydraulic pressure. Many of concrete bricks and concrete blocks machine uses vibration for completion of the process.
After that, the blocked are pushed out of the mold onto a flat steel pallet. The pallet and blocks are push out of a machine to the chain conveyor. Some of the machines have a feature of rotating brush and it removes the loose material from the top of the blocks.
3. Curing
Now the pallets of a block are conveyed to an automated stacker or loader and this places them in a curing rack. There are several hundred blocks on each rack. After the rack is full it is rolled onto a set of rails and then moved to a curing kiln.
This is the room having the capacity to hold several racks of the blocks at a time. There are mainly two types of curing is used. First is low-pressure kiln where blocks are held for one to three hours at room temperature to harden slowly. Then the steam is introduced at 60o F (16o C per hour) to raise the temperature for hardening. The standard weight blocks are cured at 150-165o F (66-74o C) and lightweight blocks are cured at 170-185o F (77-85o C). After reaching the temperature steam is shut off and blocks soaked the hot, moist air for 12-18 hours. The curing process takes about 24 hours.
The other type of kiln is high-pressure steam kiln it is also known as an autoclave. The temperature in this kiln is 300-375o F (149-191o C) and the pressure is 80-185 psi about 5.5 to 12.8 bar. The blocks are held for 5 to 10 hours. The pressure is vented and blocks release the moisture inside. The autoclave curing process is using more energy and also more expensive but it produces more blocks in less time.
4. Cubing
Racks of the cured blocks are then rolled out the kiln and the pallets of a block are unstacked and place on a chain conveyor. After that, the blocks are pushed off the steel pallets and the empty pallets are fed back to the block machine for new blocks.
If there is a split-face block, it first molded as two blocks joined. After the curing completed of double blocks, it passes through a splitter, and the heavy blade strikes between two halves.
The concrete bricks and blocks are pass through a cuber that aligns each block and stacks them into cube three blocks by six blocks deep by three or four blocks high. Then the cubes are carried outside with a forklift and store for dispatch.
Quality
Manufacturing of the concrete bricks and blocks are required to constant monitoring for producing the blocks for required properties. Raw material weighed electronically before goes to mixer. The water content in sand and gravel measured by ultrasonic sensors and how much water is required to measure automatically. For cold and warm conditions, the water has to pass through a chiller or heater before use.
After coming out of the machine the height of the block should check with laser beam sensors and in the curing chamber the temperature, pressure, and cycle time should be check properly and record automatically to ensure that the blocks should cure properly for maximum strength.